Demo:
package obj;
/**
* 多态
*/
public class Dome {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 多态的实现方式:
* 1、类型定义的是基类 Animal
* 2、实例化的是派生类 Cat
* 通过基类调用其中的方法和属性
*
* NOTE:
* 通过基类调用属性,返回的是基类中的属性
* 通过基类调用方法,返回的是子类中重写的方法
*/
//多态
Animal c = new Cat();
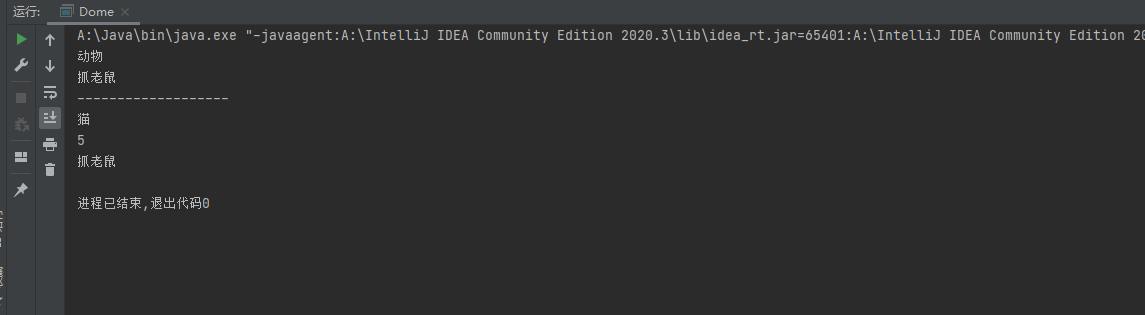
System.out.println(c.name); // 动物
//System.out.println(c.age); //报错,因为 Animal类中没有age属性
c.skill(); //抓老鼠
System.out.println("-------------------");
//正常调用方式
Cat c1 = new Cat();
System.out.println(c1.name);//猫
System.out.println(c1.age);//5 不报错,因为 Cat 类中有age属性
c1.skill();//抓老鼠
}
}
基类:
package obj;
public class Animal {
String name = "动物";
public void skill()
{
System.out.println("警惕");
}
}
派生类:
package obj;
public class Cat extends Animal{
String name = "猫";
byte age = 5;
public void skill() {
System.out.println("抓老鼠");
}
}